Silent panic attacks vs. panic attacks both involve intense feelings of fear and anxiety, but silent panic attacks do not typically exhibit physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, trembling, or sweating. Silent panic attacks are experienced internally and may include symptoms like fear of loss of control, chest pain, shaking, dizziness, difficulty breathing, increased heart rate, lightheadedness, numbness of extremities, nausea, feelings of detachment, and hot flashes.
On the other hand, panic attacks are usually more intense and can last longer, often involving physical symptoms along with psychological distress. Understanding the differences between these two types of panic experiences can help individuals recognize and effectively manage their symptoms.
Credit: www.sandstonecare.com
1. Understanding Panic Attacks
Silent panic attacks and regular panic attacks differ in their outward symptoms, with silent panic attacks lacking signs such as heart palpitations or sweating. However, internally, silent panic attacks can still cause fear, chest pain, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. It’s important to understand and recognize the hidden signs of silent panic attacks for proper management and support.
Panic attacks can be debilitating and overwhelming experiences that impact individuals both mentally and physically. Understanding the nature of panic attacks can help individuals recognize the signs, seek support, and develop effective coping strategies.
1.1 What Is A Panic Attack?
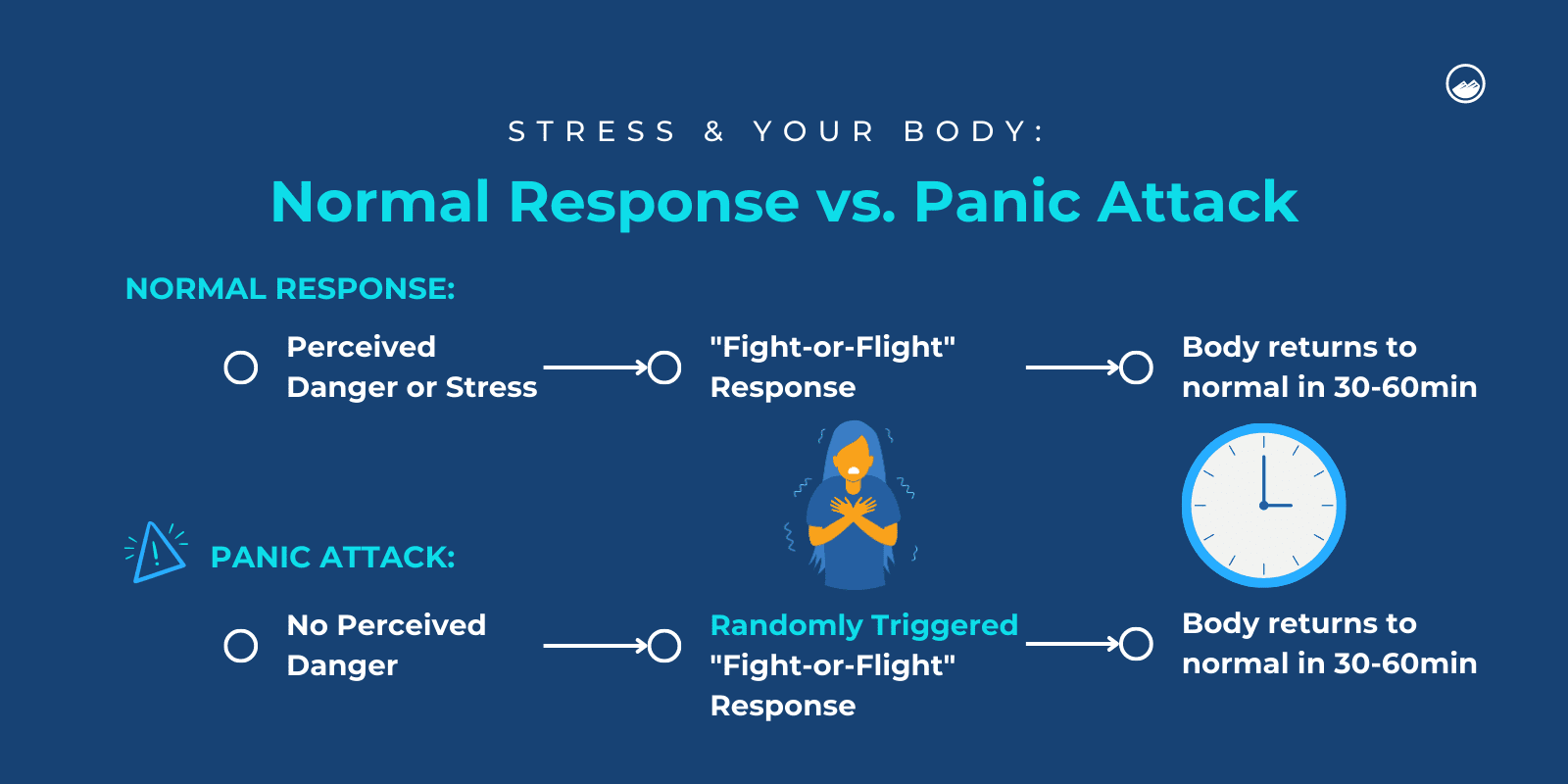
A panic attack refers to a sudden and intense surge of fear or discomfort that reaches its peak within minutes. During a panic attack, individuals may experience a combination of physical and cognitive symptoms, leading to an overwhelming sense of impending doom. It is crucial to distinguish between panic attacks and other anxiety-related conditions to ensure appropriate management and treatment.
1.2 Symptoms Of A Panic Attack
Panic attacks can manifest through various physical and cognitive symptoms, causing immense distress. Some common symptoms include:
- Racing heart or palpitations
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Trembling or shaking
- Sweating
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Nausea or stomach distress
- Hot flashes or chills
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- A sense of impending doom or loss of control
1.3 Duration Of A Panic Attack
The duration of a panic attack can vary from person to person. In general, a panic attack usually peaks within minutes and typically lasts around 20 to 30 minutes. However, some individuals may experience shorter or longer attacks depending on various factors such as the severity of the symptoms, personal triggers, and individual stress response.
2. Silent Panic Attacks
Silent panic attacks are a lesser-known but equally distressing manifestation of panic disorder. Unlike regular panic attacks, silent panic attacks do not involve the typical outward signs of anxiety, such as trembling, sweating, or heart palpitations. Instead, these attacks manifest primarily through internal symptoms, making them difficult to identify and often leaving the sufferer feeling isolated and misunderstood.
2.1 What Are Silent Panic Attacks?
Silent panic attacks are episodes of intense fear and anxiety that occur without any visible physical signs or symptoms. While regular panic attacks are characterized by outward manifestations of distress, silent panic attacks are experienced primarily as internal sensations. This means that individuals experiencing silent panic attacks may not display any noticeable signs of anxiety, making it challenging for others to recognize and offer support.
2.2 Differences Between Silent Panic Attacks And Regular Panic Attacks
While silent panic attacks and regular panic attacks share similar underlying causes and triggers, there are some key differences between the two experiences. The main distinction lies in the way these attacks manifest. Regular panic attacks typically involve noticeable physical symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and trembling. On the other hand, silent panic attacks primarily manifest internally, often causing sensations like chest pain, dizziness, difficulty breathing, increased heart rate, and numbness of extremities. These differences in symptom presentation can make silent panic attacks more difficult to diagnose and understand.
2.3 Symptoms Of Silent Panic Attacks
The symptoms of silent panic attacks often mimic those of regular panic attacks but are experienced internally rather than expressed externally. Some common symptoms of silent panic attacks include:
- Fear of loss of control
- Chest pain
- Shaking
- Dizziness
- Difficulty breathing
- Increased heart rate
- Lightheadedness
- Numbness of extremities
- Nausea
- Feelings of detachment
- Hot flashes
It’s important to remember that these symptoms may vary from person to person, and individuals experiencing silent panic attacks might not necessarily experience all of these symptoms at once. The internal nature of these attacks can make them even more challenging to identify and manage.
3. Recognizing And Managing Panic Attacks
Silent panic attacks can be just as debilitating as regular panic attacks but with different symptoms. Instead of outward signs like heart palpitations or sweating silent panic attacks manifest internally with symptoms like chest pain, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. Recognizing and managing these silent panic attacks is crucial for individuals seeking relief from their anxiety.
Panic attacks can be frightening and overwhelming, but recognizing and managing them is crucial for finding relief and regaining control. In this section, we will explore how to identify panic attack symptoms, the importance of seeking professional help, and effective coping strategies to manage panic attacks. Let’s delve deeper into these aspects.
3.1 Identifying Panic Attack Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of a panic attack is the first step toward understanding and managing this mental health condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath or hyperventilation
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Trembling or shaking
- Sweating
- Hot flashes or chills
- Nausea or stomach upset
- Feeling of impending doom
- Fear of losing control or going crazy
- Number of tingling sensations in the extremities
3.2 Seeking Professional Help
When experiencing panic attacks, seeking professional help is essential in understanding the underlying causes and developing effective strategies for management. A mental health professional, such as a therapist or psychologist, can provide valuable guidance and support. They will conduct a thorough assessment of your condition, help you identify triggers and coping mechanisms, and offer evidence-based treatments like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or medication if needed. Remember, reaching out for professional help is a proactive step towards better mental health.
3.3 Coping Strategies For Panic Attacks
Managing panic attacks is possible through various coping strategies that work to alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency and intensity of attacks. Here are some effective techniques to consider:
- Deep breathing: Practice deep breathing exercises to help regulate your breathing during a panic attack. Slowly inhale through your nose, hold your breath for a few seconds, and exhale through your mouth. This technique can help calm your nervous system and bring your body back to a relaxed state.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Engage in progressive muscle relaxation by tensing and then releasing each muscle group in your body. Start from your toes, gradually working your way up to your head. This technique helps release tension and promotes relaxation.
- Positive self-talk: Challenge negative thoughts and replace them with positive affirmations. Remind yourself that panic attacks are temporary and that you have the strength to overcome them. Repeat empowering statements such as “I am safe” or “This feeling will pass.”
- Distract yourself: Engage in activities that divert your attention away from the panic attack symptoms. Listen to calming music, solve puzzles, engage in a hobby, or practice deep breathing and visualization exercises.
- Seek support: Reach out to a trusted friend or family member who can provide emotional support during a panic attack. Having someone to talk to and lean on can help alleviate the distress.
Remember, each individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It may take time to discover the right coping strategies that resonate with you. With patience, persistence, and professional guidance, you can effectively manage and overcome panic attacks.
Credit: www.tiktok.com
4. Importance Of Addressing Panic Attacks
Addressing the importance of Silent Panic Attacks versus regular Panic Attacks is crucial as Silent Panic Attacks manifest internal symptoms that may go unnoticed. By understanding the differences and addressing these attacks, individuals can seek appropriate support and take steps toward managing their anxiety effectively.
4.1 Potential Risks Of Ignoring Panic Attacks
Ignoring panic attacks can have serious consequences for both your physical and mental well-being. When left unaddressed, panic attacks can lead to a range of potential risks, including:
- Development of anxiety disorders: Ignoring panic attacks increases the risk of developing generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, or other anxiety-related conditions. These disorders can significantly impact daily life and may require long-term treatment.
- Impaired social and occupational functioning: Frequent panic attacks can disrupt your ability to carry out everyday tasks, fulfill work responsibilities, and maintain healthy relationships. Ignoring them can lead to decreased productivity, strained interactions, and a decline in your overall quality of life.
- Missed opportunities for early intervention: Panic attacks are often a sign of an underlying mental health issue. By ignoring them, you miss the opportunity to seek early intervention and appropriate treatment, which can lead to prolonged suffering and worsening symptoms over time.
- Increased risk of comorbid conditions: Untreated panic attacks can contribute to the development of comorbid mental health conditions, such as depression or substance abuse. These conditions can further exacerbate symptoms and make recovery more challenging.
4.2 Understanding The Impact Of Panic Attacks On Mental Health
Panic attacks can have a profound impact on your mental health. They can cause intense feelings of fear, helplessness, and impending doom, leading to a variety of emotional and psychological consequences. Understanding the impact of panic attacks on mental health is crucial for recognizing the importance of addressing them. Some key aspects to consider include:
- Increased risk of developing mental health disorders: Panic attacks are often associated with the development of various mental health disorders, including panic disorder, agoraphobia, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Addressing panic attacks promptly can help prevent the onset of these conditions.
- Interference with daily functioning: Panic attacks can disrupt your ability to engage in regular activities, attend social events, or perform at work or school. This interference can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and a diminished sense of self-worth.
- Heightened levels of anxiety and stress: Experiencing panic attacks can significantly increase overall anxiety levels, making it difficult to cope with everyday stressors. It can create a constant state of apprehension, making it hard to relax and enjoy life.
- Impact on self-esteem: Panic attacks can erode self-confidence and self-esteem, as individuals may feel embarrassed, ashamed, or weak because of their symptoms. This negative self-perception can further perpetuate anxiety and hinder recovery.
4.3 Improving Quality Of Life Through Treatment And Self-care
Addressing panic attacks is crucial for improving your quality of life. Seeking appropriate treatment and practicing self-care can make a significant difference in managing symptoms and achieving overall well-being. Here are some effective strategies for addressing panic attacks:
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of psychotherapy can help you understand and manage panic attacks by identifying triggers, challenging negative thought patterns, and developing coping strategies. Therapy provides a safe space to explore your emotions and learn healthy ways to respond to panic attacks.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to alleviate the symptoms of panic attacks. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and beta-blockers are commonly used to help regulate mood, reduce anxiety, and prevent future panic attacks.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the prevention and management of panic attacks. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, stress management techniques (such as meditation or deep breathing exercises), and adequate sleep can all contribute to overall well-being and reduce the frequency and intensity of panic attacks.
- Support network: Building a strong support network of family, friends, or support groups can provide emotional support, encouragement, and understanding during the process of addressing panic attacks. Connecting with others who have had similar experiences can also provide valuable insights and coping strategies.
By recognizing the potential risks of ignoring panic attacks, understanding their impact on mental health, and embracing appropriate treatment and self-care practices, you can take a proactive approach towards addressing and managing panic attacks, leading to an improved quality of life.

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Silent Panic Attacks Vs. Panic Attacks
What Does A Silent Panic Attack Look Like?
A silent panic attack may not have visible symptoms but can include internal feelings of fear, chest pain, shaking, dizziness, difficulty breathing, increased heart rate, numbness, nausea, and hot flashes. It is important not to ignore these symptoms as they may mimic other ailments.
What Happens If You Ignore A Panic Attack?
Ignoring a panic attack is not recommended. It’s important to pay attention to the symptoms, as they may resemble other ailments and could be a sign of something more serious, like a heart attack. Seek help and manage panic attacks instead of ignoring them.
How Long Can Silent Panic Attacks Last?
Silent panic attacks can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
Conclusion
Silent panic attacks and panic attacks may have similar underlying causes, but they differ in their manifestation of symptoms. While panic attacks are characterized by intense physical and psychological symptoms, silent panic attacks are internal and may not exhibit noticeable signs to others.
It is important to recognize and understand both types of attacks to provide the appropriate support and care for individuals experiencing them. By raising awareness and promoting mental health education, we can create a more empathetic and supportive society for those dealing with anxiety disorders.
Let’s prioritize mental well-being and work towards destigmatizing these conditions.
